- Messages
- 58
- Reaction score
- 7
- Points
- 18
We are currently struggling to cover the operational costs of Xtremepapers, as a result we might have to shut this website down. Please donate if we have helped you and help make a difference in other students' lives!
Click here to Donate Now (View Announcement)
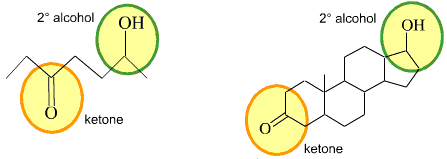
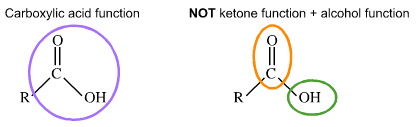
For almost 10 years, the site XtremePapers has been trying very hard to serve its users.
However, we are now struggling to cover its operational costs due to unforeseen circumstances. If we helped you in any way, kindly contribute and be the part of this effort. No act of kindness, no matter how small, is ever wasted.
Click here to Donate Now