- Messages
- 1,594
- Reaction score
- 483
- Points
- 93
AOA! 
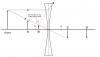
I could not understand question 22 of this paper: http://www.xtremepapers.net/CIE/Cambrid ... 9_qp_1.pdf
Maybe that's because I do not know the properties of a diverging lens. Can anyone help me out please?
JazakAllah!
I could not understand question 22 of this paper: http://www.xtremepapers.net/CIE/Cambrid ... 9_qp_1.pdf
Maybe that's because I do not know the properties of a diverging lens. Can anyone help me out please?
JazakAllah!