- Messages
- 1,558
- Reaction score
- 2,428
- Points
- 273
ikr, but the question has in it a diagram. =/type the question as this ppr is not present in xtremepprz
We are currently struggling to cover the operational costs of Xtremepapers, as a result we might have to shut this website down. Please donate if we have helped you and help make a difference in other students' lives!
Click here to Donate Now (View Announcement)
ikr, but the question has in it a diagram. =/type the question as this ppr is not present in xtremepprz
because the chromosomes number remains the same after mitosis, i.e 46 in humans. unlike meiosis where the chromosome number halves after the cell replication. it can't be a homologous pair caz mitosis is taking place not meiosis, dre needs to be passing of the same characteristics and features which the parent cell had to the daughter cells hence A is correct..http://www.xtremepapers.com/CIE/International A And AS Level/9700 - Biology/9700_s03_qp_1.pdf
can anyone explain why the answer to q16 is A and not B?
Xylem vessels are dead cells , with lignified walls (except at the plasodesmata) whereas sieve tubes elements are living cells (but devoid of nuclei and ribosomes) and donot have lignified wallsWhat are the differences and similarities between the xylem vessels and sieve tubes?
give a brief explanation for the differences in structure.
maybe because larger animals are comparatively less active whereas smaller animals and insects need to efficiently transport oxygen to all part of the body due to their very active living..:/http://www.xtremepapers.com/CIE/International A And AS Level/9700 - Biology/9700_s04_qp_1.pdf
explain question 30 anyone ? ^^
the pathogens which cause different diseases, mode of transmition, global pattern of dat disease, how to eradicate or prevent those diseases etc....check the syllabus man...can someone please tell me what exactly do we need to know from the chapter infectious diseases. Do we need to know how the diseases were spread in the past and the dates and countries and all that? or just an outline of the diseases history? because my text book has so much information about the history of the disease where it originated from the years and the graphs and census done on the diseases world wide its too much info and i dont want to study it all if its not required so plss can someone tell me? this is for As btw
Also if any of youll have notes for that chapter would be really great
please and thank you
go through the syllabus and past papers!can someone please tell me what exactly do we need to know from the chapter infectious diseases. Do we need to know how the diseases were spread in the past and the dates and countries and all that? or just an outline of the diseases history? because my text book has so much information about the history of the disease where it originated from the years and the graphs and census done on the diseases world wide its too much info and i dont want to study it all if its not required so plss can someone tell me? this is for As btw
Also if any of youll have notes for that chapter would be really great
please and thank you
Hi, Need help!
As and Alevel Biology book by Marry Jones. Endorsed By Cambridge..
Chapter 9 ''The Mammalian Heart''
Q.number 9.1 SAQ b and c part
Ch 8 ''The mammalian transport system'' : SAQ Q. 8.13 regarding dissociation curve
Can you give a comparison between arteries veins and capillaries ..? Thank you.
Indeed it helps!For the comparison between arteries veins and capillaries :
Artery:
- Thick muscular wall
-Much elastic tissue
-Small lumen relative to diameter
-Capable of constriction
- Not permeable
- Valves in aorta and pulmonary artery only
- transport blood from the heart
-Oxygenated blood expect in pulmonary artery
-Blood under high pressure (10- 16 kPa)
-Blood moves in pulses
-Blood flows rapidly
Vein:
-Thin muscular wall
-Little elastic tissue
-Large lumen relative to diameter
-Not capable of constriction
-Not permeable
-Valves thoughout all veins
-Transport blood to heart
-Deoxygenated blood except in pulmonary vein
-Blood under low pressure (1kPa)
-No pulses
-Blood flows slowly
Capillary:
-No muscles
-No elastic tissue
-Large lumen relative to diameter
-Not capable of constriction
-Permeable
-No valves
-Links arteries to veins
-Blood changes from oxygenated to deoxygenated
-Blood pressure reducing (4-1 kPa)
-No pulses
-Blood flow slowing
Hope it Helps !
answers are given at the back.As and Alevel Biology book by Marry Jones. Endorsed By Cambridge..
Chapter 9 ''The Mammalian Heart''
Q.number 9.1 SAQ b and c part
a(i) from the curve ( and also the table given below) 96.5%As and Alevel Biology book by Marry Jones. Endorsed By Cambridge..
Ch 8 ''The mammalian transport system'' : SAQ Q. 8.13 regarding dissociation curve
really i never checked end of the bookanswers are given at the back.
still, 9.1 (b) ventricular systole will be when pressure rise is greatest., dat is from about 0.15 to 0.45 which is the time of closing and opening of atrio-ventricular valves respectively.
when the ventricular systole is over, ventricle relax, i.e. its diastole. this is from about 0.45 to approx 0.7s.
(c) atria contracts after ventricular diastole, and the pressure change will be smaller this tym so both frm 0 to 0.15 and 0.7 to 0.85 are atrial systoles.
i am not sure about (ii) but as far as i've known, ventricular diastole and atrial diastole occur at the same time. this is when atria are filled. so probably this will be same as b(ii).
this also might help.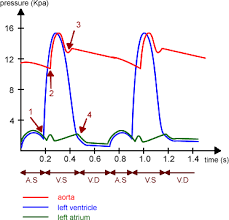
it was easya(i) from the curve ( and also the table given below) 96.5%
(ii)fully saturated means 100%, so by unitary method,
%age : vol. of O2
100 : 1.3
96.5 : x
x = (96.5 * 1.3 )/ 100 = 1.25 cm^3
b(i) 24%
(ii) again the method above, vol. of O2= (24 * 1.3)/100 = 0.312 cm^3
For more than 16 years, the site XtremePapers has been trying very hard to serve its users.
However, we are now struggling to cover its operational costs due to unforeseen circumstances. If we helped you in any way, kindly contribute and be the part of this effort. No act of kindness, no matter how small, is ever wasted.
Click here to Donate Now