- Messages
- 99
- Reaction score
- 23
- Points
- 8
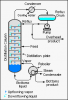
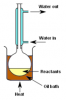
Bingo. Both involve a condenser, distillation is a separation technique.Preventing loss of volatile substances would be reflux. Distillation would be something you do after the reaction is complete to separate the reactants and products. No? At least that's what I thought.
I'm asking not telling btw. I'm pretty confused right now.