- Messages
- 216
- Reaction score
- 334
- Points
- 73
We are currently struggling to cover the operational costs of Xtremepapers, as a result we might have to shut this website down. Please donate if we have helped you and help make a difference in other students' lives!
Click here to Donate Now (View Announcement)
wow that helped ALOT m8 and the graphs are more than enough.....now i gotta doubt on the imposition of tax.....why does the consumer wish to buy the same number of quantity he purchased before the tax? like for the answer of the first question why isn't the answer WX isn't that the diff between the s1 and s2?....and again thx
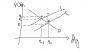
1)explain the effects of the removal of indirect tax in the market for a product? (8)
2)discuss whether an indirect tax is a satisfactory way to tackle negative externalities like air pollution?(12)
i kinda know the structure on how to answer this but can anyone share with me how they would answer this question in a way to achieve the maximum of marks?
wow.....good answers
For almost 10 years, the site XtremePapers has been trying very hard to serve its users.
However, we are now struggling to cover its operational costs due to unforeseen circumstances. If we helped you in any way, kindly contribute and be the part of this effort. No act of kindness, no matter how small, is ever wasted.
Click here to Donate Now