- Messages
- 59
- Reaction score
- 89
- Points
- 28
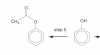
when the double bond between 2 carbons will break CO2 will be released.
when the double bond between carbon which is attached to methyl group breaks CH3COH is formed which is furthur oxidised to CH3COOH acid,another organic product.
Hope this will help.
when the double bond between carbon which is attached to methyl group breaks CH3COH is formed which is furthur oxidised to CH3COOH acid,another organic product.
Hope this will help.