-
We need your support!
We are currently struggling to cover the operational costs of Xtremepapers, as a result we might have to shut this website down. Please donate if we have helped you and help make a difference in other students' lives!
Click here to Donate Now (View Announcement)
You are using an out of date browser. It may not display this or other websites correctly.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
help needed in physics!!
- Thread starter larina
- Start date
1) the cathode is heated to produce electrons (cathode rays)
2) the grid hole and its negative potential control the amount of electrons passing through it (to control the brightness)
3) the highly positive anode system accelerates the electrons, and has three annular rings to produce a narrow fast beam of electrons.
they accelerate and focus the electrons to narrow a beam.
4) the fast electron beam strikes the fluorescent screen producing a bright positive spot.
5) the electric potential on Y-plates can deflect the beam in a vertical direction (up & down)
6) the electric potential on X-plates deflects the beam in a horizontal direction (right & left)
How it works:
a)time base circuit: a sweep generator connected to the X-plates, it moves the spot horizontally across the screen and repeats it at a certain frequency "f". the time taken by the spot to cross the screen diameter is the periodic time "T", where T= 1/f
b) the voltage to be studied is applied to the Y-plates
c) the combined sweep and Y-voltages produce a graph showing the variation of voltage with time
Uses:
1) can be used to measure as a voltmeter by measuring the deflection in Y-direction in cm, then multiplying it by the value of "Y-sensitivity" control to change it to volts.
eg. if the peak height in Y-direction is 4 cm and the sensitivity is 5V/cm, the voltage : 4cm * 5 V/cm = 20 V
2) the X-axis is used to measure the time. the time-base control is used to calibrate the X-axis and change the distance in X-direction to time interval.
eg. a sensitivity of 0.05 s/cm means that each 1 cm on X-axis represents 0.05 seconds. If the length of a wave on the screen is 8cm, then
the periodic time, T=8cm * 0.05 s/cm = 0.4 sec.
the frequency, f=1/T = 1/0.4 = 2.5 Hz
hope this helps
2) the grid hole and its negative potential control the amount of electrons passing through it (to control the brightness)
3) the highly positive anode system accelerates the electrons, and has three annular rings to produce a narrow fast beam of electrons.
they accelerate and focus the electrons to narrow a beam.
4) the fast electron beam strikes the fluorescent screen producing a bright positive spot.
5) the electric potential on Y-plates can deflect the beam in a vertical direction (up & down)
6) the electric potential on X-plates deflects the beam in a horizontal direction (right & left)
How it works:
a)time base circuit: a sweep generator connected to the X-plates, it moves the spot horizontally across the screen and repeats it at a certain frequency "f". the time taken by the spot to cross the screen diameter is the periodic time "T", where T= 1/f
b) the voltage to be studied is applied to the Y-plates
c) the combined sweep and Y-voltages produce a graph showing the variation of voltage with time
Uses:
1) can be used to measure as a voltmeter by measuring the deflection in Y-direction in cm, then multiplying it by the value of "Y-sensitivity" control to change it to volts.
eg. if the peak height in Y-direction is 4 cm and the sensitivity is 5V/cm, the voltage : 4cm * 5 V/cm = 20 V
2) the X-axis is used to measure the time. the time-base control is used to calibrate the X-axis and change the distance in X-direction to time interval.
eg. a sensitivity of 0.05 s/cm means that each 1 cm on X-axis represents 0.05 seconds. If the length of a wave on the screen is 8cm, then
the periodic time, T=8cm * 0.05 s/cm = 0.4 sec.
the frequency, f=1/T = 1/0.4 = 2.5 Hz
hope this helps
- Messages
- 102
- Reaction score
- 0
- Points
- 26
thnx bro n thnx larina 4 postin ds thread!!!
- Messages
- 102
- Reaction score
- 0
- Points
- 26
mm although i gt a hard on while studyin CRO yet i had no intention of askin bout it on XPF bt as u introducd ds post so i got a chance 2 understand it!!!!! 
- Messages
- 102
- Reaction score
- 0
- Points
- 26
A potentiometer is a manually adjustable resistor. The way this device works is relatively simple. One terminal of the potentiometer is connected to a power source. Another is hooked up to ground (a point with no voltage or resistance and which serves as a neutral reference point), while the third terminal runs across a strip of resistive material. This resistive strip generally has a low resistance at one end; its resistance gradually increases to a maximum resistance at the other end. The third terminal serves as the connection between the power source and ground, and is usually interfaced to the user by means of a knob or lever. The user can adjust the position of the third terminal along the resistive strip in order to manually increase or decrease resistance. By controlling resistance, a potentiometer can determine how much current flows through a circuit. When used to regulate current, the potentiometer is limited by the maximum resistivity of the strip.
there are a lot of different applications for the potentiometer, but in order for you to understand them i need to show you diagrams, the basic idea of it though is how a thermistor or an LDR can turn on or off a lamp/alarm..etc by different conditions depending on resistances and external conditions, if you want send me your email and I'll take pictures of my notes and email them to you with the explanation.
PlanetMaster
XPRS Administrator
- Messages
- 1,177
- Reaction score
- 2,109
- Points
- 273
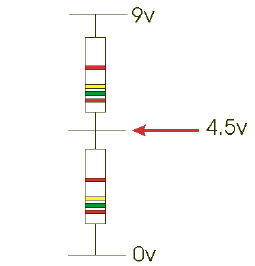
Potential Dividers:
When two resistors of equal value are connected across a supply, current will flow through them. If a meter is placed across the supply shown in the diagram it will register 9v. If the meter is then placed between the 0v and the middle of the two resistors it will read 4.5v. The battery voltage has been divided in half.
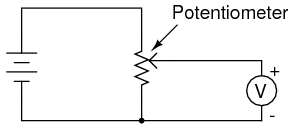
Potentiometer:
Potentiometers are variable voltage dividers with a shaft or slide control for setting the division ratio.
When two resistors of equal value are connected across a supply, current will flow through them. If a meter is placed across the supply shown in the diagram it will register 9v. If the meter is then placed between the 0v and the middle of the two resistors it will read 4.5v. The battery voltage has been divided in half.

Potentiometer:
Potentiometers are variable voltage dividers with a shaft or slide control for setting the division ratio.

PlanetMaster
XPRS Administrator
- Messages
- 1,177
- Reaction score
- 2,109
- Points
- 273
Then the voltage is in ratio to its resistance.
- Messages
- 102
- Reaction score
- 0
- Points
- 26
@palnet master:so was my discription rong kindly explain a bit more
- Messages
- 102
- Reaction score
- 0
- Points
- 26
@mufti i dnt think k according to planet masters description it is rheostat!!!!
PlanetMaster
XPRS Administrator
- Messages
- 1,177
- Reaction score
- 2,109
- Points
- 273
A rheostat is a Potentiometer.
Potential divider's vary voltages in small intervals like 2v,4v,6v and so on
while Potentiometers vary voltages with much smaller intervals like 0.1v, 0.2v, 0.3v and so on.
Potential divider's vary voltages in small intervals like 2v,4v,6v and so on
while Potentiometers vary voltages with much smaller intervals like 0.1v, 0.2v, 0.3v and so on.