- Messages
- 1,394
- Reaction score
- 1,377
- Points
- 173
Suchal Riaz yeah u can do it now.. i thought maybe u had chemistry paper so i said that u cud do it after that...
i'll be waiting... thanks a lot for ur help man!
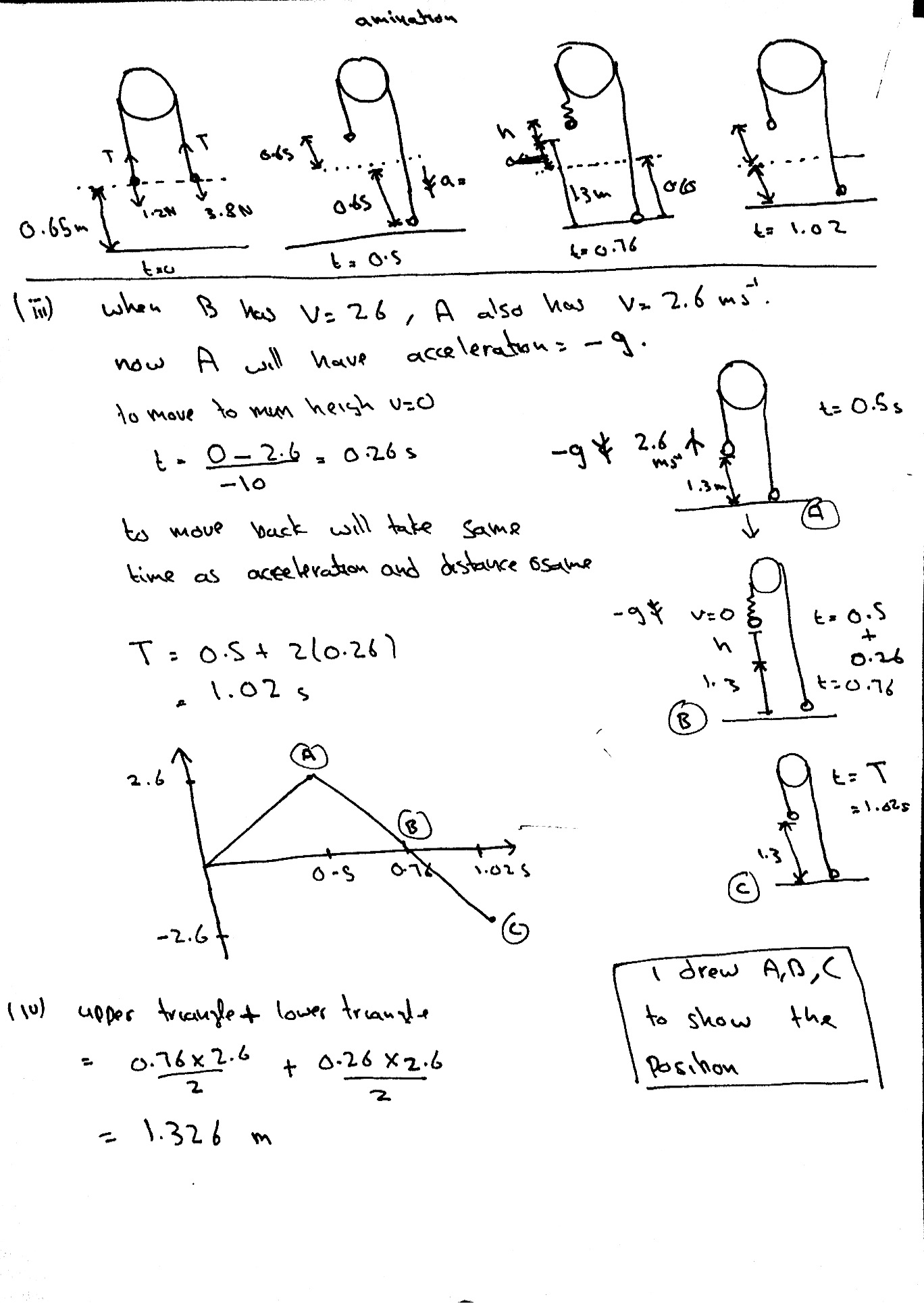
this is the one concept in the pulleys topic that is not going that well for me... :/
i'll be waiting... thanks a lot for ur help man!
this is the one concept in the pulleys topic that is not going that well for me... :/