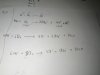- Messages
- 2
- Reaction score
- 0
- Points
- 1
The gas is behaving ideally, use PV=nRT before and after compression and make n the subject. You'll see that for both equations n is constant.in an experiment a sample of a pure gas is put into a gas syringe at a temperature of 300K and pressure of 16 kpa. the gas is compressed until the volume occupied by the gas is halved.
after the compression, the temperature of the gas in syringe is 375 and the pressure is 40 kpa.
is the gas is ideal