Yes.Ans fr Q3 is C?
-
We need your support!
We are currently struggling to cover the operational costs of Xtremepapers, as a result we might have to shut this website down. Please donate if we have helped you and help make a difference in other students' lives!
Click here to Donate Now (View Announcement)
You are using an out of date browser. It may not display this or other websites correctly.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
Chemistry: Post your doubts here!
- Thread starter XPFMember
- Start date
- Messages
- 249
- Reaction score
- 419
- Points
- 73
Well yu see at the first glimpse of the question yu should make out tht D is incorrect as the Cs and Na is in same groupYes.
the charges wont also affect since Cs and Na hav the same charge
the only thing tht is valid is tht Cs is quite a large sized atom, comparatively so the Ionic radius should be the ans
- Messages
- 64
- Reaction score
- 126
- Points
- 18
- Messages
- 59
- Reaction score
- 89
- Points
- 28
for Q 21 it is B
For Q 26 its D because it is tertiary and opens to only SN1 reaction whose rate only depends on conc. of Halogenoalkane
For Q 25 Cl atom can replace any H on carbon atom so it can replace 4 atoms anyone at a time
Hope this helps
For Q 26 its D because it is tertiary and opens to only SN1 reaction whose rate only depends on conc. of Halogenoalkane
For Q 25 Cl atom can replace any H on carbon atom so it can replace 4 atoms anyone at a time
Hope this helps
- Messages
- 297
- Reaction score
- 696
- Points
- 93
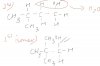
For Q5,The answer is BPlease guys help especially with 5. For 26 ans is D but B also forms secondary carbocation and it could be stable as well like in sn2 mechanisms so why it isn't B?
View attachment 45107 View attachment 45108 View attachment 45109 View attachment 45110
This Question is simple,but tricky
Lsn...The Enthalpy change to convert I2 from solid to gas is +38 KJ mol^-1 (GIVEN)
The Enthalpy change for the reaction of I2(g) with Cl2 is -214 KJ mol^-1 (GIVEN)
Wat is the definition of enthalpy change of formation of ICl3?? it is when i mol of a ICl3 is produced from its elements
The enthalpy change for the production of 2ICl3 is = +38 - 214 = -176 KJ mol^-1
2 ICl3 --------> - 176
1 ICl3 --------> -176 /2 = - 88 KJ mol^-1
Hope this helps
- Messages
- 297
- Reaction score
- 696
- Points
- 93
MAn could u plz include the answers next timePlease guys help especially with 5. For 26 ans is D but B also forms secondary carbocation and it could be stable as well like in sn2 mechanisms so why it isn't B?
View attachment 45107 View attachment 45108 View attachment 45109 View attachment 45110
BEST OF LUCK
- Messages
- 59
- Reaction score
- 130
- Points
- 43
http://papers.xtremepapers.com/CIE/... AS Level/Chemistry (9701)/9701_s13_qp_12.pdf
Number 40?? Answer is D
Number 40?? Answer is D
- Messages
- 872
- Reaction score
- 894
- Points
- 103
Yeah I got as much, but in the answer the double bond isn't found there. It's to the left of the bond that u drew as the double bondWith conc. H2SO4, dehydration will occur. The OH of alcohol plus a H from neighbouring C is lost forming a double bond. Hope the picture helps.View attachment 45099
- Messages
- 64
- Reaction score
- 126
- Points
- 18
sorry about that if i include answers then brain will automatically make logic to make the answer correct so i may not get good explanation happens to me but you guys rock! sure from next timeMAn could u plz include the answers next time
BEST OF LUCK
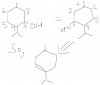
why is 21 B?? i get that two different products are formed but arent both undergoing elimination?? and i dont get 25 clearly please elaborate thanks!!for Q 21 it is B
For Q 26 its D because it is tertiary and opens to only SN1 reaction whose rate only depends on conc. of Halogenoalkane
For Q 25 Cl atom can replace any H on carbon atom so it can replace 4 atoms anyone at a time
Hope this helps
Last edited:
I have doubts on 5,25 too.Please guys help especially with 5. For 26 ans is D but B also forms secondary carbocation and it could be stable as well like in sn2 mechanisms so why it isn't B?
View attachment 45107 View attachment 45108 View attachment 45109 View attachment 45110
For 21, first draw the displayed formula. When alcohol is reacted with conc. H2SO4, dehydration should occur. However, for the first isomer there is no neighbouring CH from where the H could be taken. 2nd isomer can be easily dehydrated, as shown in the picture.
For 26, secondary carbocation can either undergo SN1 or SN2 mechanism, so it is better you go with the last option, the third degree halogenation.
It's the same. 
Yeah I got as much, but in the answer the double bond isn't found there. It's to the left of the bond that u drew as the double bond
- Messages
- 872
- Reaction score
- 894
- Points
- 103
Is 25 C?Please guys help especially with 5. For 26 ans is D but B also forms secondary carbocation and it could be stable as well like in sn2 mechanisms so why it isn't B?
View attachment 45107 View attachment 45108 View attachment 45109 View attachment 45110
Bro, can you explain how enthalpy change of prod. Is 38-214?For Q5,The answer is B
This Question is simple,but tricky
Lsn...The Enthalpy change to convert I2 from solid to gas is +38 KJ mol^-1 (GIVEN)
The Enthalpy change for the reaction of I2(g) with Cl2 is -214 KJ mol^-1 (GIVEN)
Wat is the definition of enthalpy change of formation of ICl3?? it is when i mol of a ICl3 is produced from its elements
The enthalpy change for the production of 2ICl3 is = +38 - 214 = -176 KJ mol^-1
2 ICl3 --------> - 176
1 ICl3 --------> -176 /2 = - 88 KJ mol^-1
Hope this helps
- Messages
- 64
- Reaction score
- 126
- Points
- 18
yes how?Is 25 C?
- Messages
- 872
- Reaction score
- 894
- Points
- 103
No if you drew the double bond between carbons 3 and 4, the actual double bond is between carbons 4 and 5. You drew it to the right if the side chain...it's actually exactly on the other side of the side chainIt's the same.
- Messages
- 64
- Reaction score
- 126
- Points
- 18
Yeah man explained like a boss thank you a lot!I have doubts on 5,25 too.
For 21, first draw the displayed formula. When alcohol is reacted with conc. H2SO4, dehydration should occur. However, for the first isomer there is no neighbouring CH from where the H could be taken. 2nd isomer can be easily dehydrated, as shown in the picture.
View attachment 45112
For 26, secondary carbocation can either undergo SN1 or SN2 mechanism, so it is better you go with the last option, the third degree halogenation.
- Messages
- 872
- Reaction score
- 894
- Points
- 103
You can remove a hydrogen from any if the side chains, CH3, CH3, CH3 and C2H5, but if you remove it from the methyl groups that aren't in the main chain but are attached as a side chain to carbon 2, you end up with the same productyes how?
- Messages
- 64
- Reaction score
- 126
- Points
- 18
thought so but had doubts thanks for clearing..You can remove a hydrogen from any if the side chains, CH3, CH3, CH3 and C2H5, but if you remove it from the methyl groups that aren't in the main chain but are attached as a side chain to carbon 2, you end up with the same product
- Messages
- 5,330
- Reaction score
- 11,839
- Points
- 698
http://papers.xtremepapers.com/CIE/...d AS Level/Chemistry (9701)/9701_s09_qp_1.pdf
q15- A
q20-c
p.s: any notes on oxidation states in complex ions, really need it :S
q15- A
q20-c
p.s: any notes on oxidation states in complex ions, really need it :S