- Messages
- 20
- Reaction score
- 4
- Points
- 13
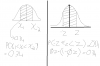
Eight cards are selected with replacement from a standard pack of playing cards
with 12 pic cards, 20 odd cards
and 20even cards.
a) how many different sequences of cards are possible?
b) how many of the sequencees in part (a) will contain three picture cards, three odd cars and two even cards??
with 12 pic cards, 20 odd cards
and 20even cards.
a) how many different sequences of cards are possible?
b) how many of the sequencees in part (a) will contain three picture cards, three odd cars and two even cards??