- Messages
- 16
- Reaction score
- 0
- Points
- 1
We are currently struggling to cover the operational costs of Xtremepapers, as a result we might have to shut this website down. Please donate if we have helped you and help make a difference in other students' lives!
Click here to Donate Now (View Announcement)
I= a^2Why is the answer A:-
View attachment 22139
as we know that frequency of fundamental is fWhy is the answer D:-
View attachment 22147
You cannot use the actual capacitance of X for the first part because you don't know the don't know the potential difference across X. So it is easier to use the effective capacitance and the total potential difference. Otherwise you can also do it by the longer method if you want to use the actual capacitance.
First calculate the potential difference cross X.
Total resistance in series is 12 micro farad and 24 micro farad from the parallel combination. So, potential across X=
(capacitance of X/ total capacitance in series) * 9
(1/12)/(1/12+1/24) * 9 = 6v
Now use Q =CV for X
Q = 12 micro farad * 6 =7.2* 10^-5 =72 micro C
You get the same answer, just a longer calculation.
For Y you can use the actual capacitance because you already know the potential difference cross Y from your previous calculations.
look buddy this question need some focus the wall is rough but the floor is notThe Answer will be B that i think so,PLEASE do tell me if i am right?
A: In A weight is acting downward and the normal reaction force at the end of ladder is upward and the force P is the normal reaction force by the wall in straight direction.Which means the ladder is not sliding and on the equilibrium postion
B: In B weight is acting downward and the normal reaction force at the end of ladder is upward and the force P force P is acting slightly upward because the ladder is sliding .
C: In C weight is acting downward again and the normal reaction force at the end of ladder is now not acting against the direction of weight it is slighlt inward.
D : In D weight is acting downward again and the normal reaction force at the end of ladder is again not acting against the direction of weight it is slightly Outward
Thus the Answer will be B
Sorry, but farad is resistance? I thought it was the capacitance. So you can use it to calculate p.d. just like actual resistance?
Q = neWhy is the answer C:-
View attachment 22151
Why did they give the cross section of the wire then?Q = ne
Q = It
ne = It
n(1.6*10^-19) = (10)(1)
n = 6.3*10^19
d sin theta= n lambdaWhy is the answer D:-
View attachment 22149
Can u tell, which year it is from? and the answer?Can any solve my question?
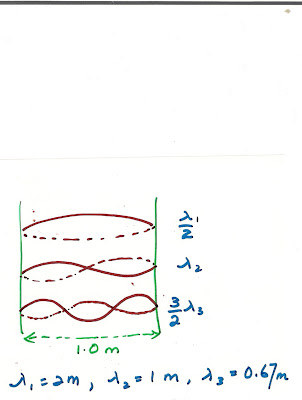
A taut wire is clamped at two points 1.0m apart.It is plucked near one end.which are three longest wavelengths on the vibrating wire?
A: 1.0m, 0.50m, 0.25m
B: 1.0m, 0.67m, 0.50m
C; 2.0m, 0.67m, 0.40m
D: 2.0m, 1.0m, 0 .50m
E: 2.0m, 1.0m, 0.67m
june 83Can u tell, which year it is from? and the answer?
FUNDAMENTAL SECOND HARMONIC AND THIRD HARMONIC ARECan any solve my question?
A taut wire is clamped at two points 1.0m apart.It is plucked near one end.which are three longest wavelengths on the vibrating wire?
A: 1.0m, 0.50m, 0.25m
B: 1.0m, 0.67m, 0.50m
C; 2.0m, 0.67m, 0.40m
D: 2.0m, 1.0m, 0 .50m
E: 2.0m, 1.0m, 0.67m
Forget the photoelectric effect for a moment. Think about what is meant by the intensity of the radiation of the target surface.Hi. I have a doubt in Photoelectric effect. I don't understand how the photoelectric current reduces when we reduce the wavelength.
Qs. 7C http://papers.xtremepapers.com/CIE/Cambridge International A and AS Level/Physics (9702)/9702_s11_qp_41.pdf
For more than 16 years, the site XtremePapers has been trying very hard to serve its users.
However, we are now struggling to cover its operational costs due to unforeseen circumstances. If we helped you in any way, kindly contribute and be the part of this effort. No act of kindness, no matter how small, is ever wasted.
Click here to Donate Now