- Messages
- 96
- Reaction score
- 221
- Points
- 33
Alright then!! I'll take that into considerationSorry, I am busy preparing for my mocks
We are currently struggling to cover the operational costs of Xtremepapers, as a result we might have to shut this website down. Please donate if we have helped you and help make a difference in other students' lives!
Click here to Donate Now (View Announcement)
Alright then!! I'll take that into considerationSorry, I am busy preparing for my mocks
What about tomorrow? I'll either inbox you or post them here with a quote to your message?What about the notes on uncertainty ??
Alright then!! I'll take that into consideration
Oh yeah!What about tomorrow? I'll either inbox you or post them here with a quote to your message?
i recommend that you post them here > so me and others can benfitWhat about tomorrow? I'll either inbox you or post them here with a quote to your message?
Hahahahaha sure!! I'll be more than glad to help out all the innocent students being tortured by CIEi recommend that you post them here > so me and others can benfit
u are too one of usHahahahaha sure!! I'll be more than glad to help out all the innocent students being tortured by CIE
yessss!! thanks for the reminder!!u are too one of us
yessss!! thanks for the reminder!!
fellas!! I too can feel your pain!!
http://papers.xtremepapers.com/CIE/Cambridge International A and AS Level/Physics (9702)/9702_w09_qp_41.pdf
http://papers.xtremepapers.com/CIE/Cambridge International A and AS Level/Physics (9702)/9702_w09_ms_41.pdf
Q-8 cii
http://papers.xtremepapers.com/CIE/Cambridge International A and AS Level/Physics (9702)/9702_s09_qp_4.pdf
http://papers.xtremepapers.com/CIE/Cambridge International A and AS Level/Physics (9702)/9702_s09_ms_4.pdf
Q-9 b.. and Q-11 biii
Can anyone help me with these.

your 3rd question is similar to 1st question. Here instead of the ratio, you are asked to find the time taken to reach that ratio
If you have understood my answer to first question it's easy to find the result for third question. But if you still have confuson then let me know.
I'll skip numerical calculations for your 4th question
Consider Initial activity is A1
after time t, Activity reduces to (A1 x 1/10)
put the values in the equation of activity
you have already found decay constant in previous parts
now just put the values and solve it.
If you are still unsure or confused about any of the answers, then let me knowI'll be glad to help

u got fx8991es-plus ??
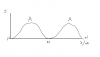
7biii)7 b iii, c
http://papers.xtremepapers.com/CIE/Cambridge International A and AS Level/Physics (9702)/9702_s05_qp_2.pdf
Please, I dont get it
For more than 16 years, the site XtremePapers has been trying very hard to serve its users.
However, we are now struggling to cover its operational costs due to unforeseen circumstances. If we helped you in any way, kindly contribute and be the part of this effort. No act of kindness, no matter how small, is ever wasted.
Click here to Donate Now