ooh....thnks
-
We need your support!
We are currently struggling to cover the operational costs of Xtremepapers, as a result we might have to shut this website down. Please donate if we have helped you and help make a difference in other students' lives!
Click here to Donate Now (View Announcement)
You are using an out of date browser. It may not display this or other websites correctly.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
Physics: Post your doubts here!
- Thread starter XPFMember
- Start date
yes it's AIs the answer A ??
Answer is B but I don't know howAnswer is B from my side... But let her answer if it is A or B
- Messages
- 90
- Reaction score
- 34
- Points
- 28
vertical velocity= u cos 45
horizontal velocity = u sin 45
so, initial K.E. : the vertical and horizontal components of kinetic energy = 1/2 m ( u cos 45 ) + 1/2 m ( u sin 45 ) ......... ( 1/2 m v^2 formula )
so, sin 45 = 0.71
....cos 45 = 0.71 ( check them in the calculator )
so they will give the same kinetic energy for both velocities ( horizontally and vertically )
so at the highest point, (theta) = 90 ( for the vertical velocity ) , horizontal velocity doesn't change
so final kinetic energy = 1/2 m ( u cos 90 ) + 1/2 m ( u sin 45 )..................... ( horizontal velocity is constant ) ( cos 90 is 0 )
final kinetic energy = 1/2 m ( u sin 45 ) + 0 only which is half of the initial kinetic energy.
- Messages
- 1,764
- Reaction score
- 3,472
- Points
- 273
Q3
answer will be B
A is Z=Y-X
B is Z=X-Y
C is Y+X
D is -X-Y
Q4
and being precise is having values 'any' values close to each other
They have asked NOT accurate so not A and B
The C values are not close to each other while the D values are
- Messages
- 90
- Reaction score
- 34
- Points
- 28
- Messages
- 1,764
- Reaction score
- 3,472
- Points
- 273
density=mass/volume
total mass will be 3.5*10^-25* 8 for 1 cube
and so Volume=9.2*10^-25 * 8/(9.2*10^3)
this will give the volume cube root the volume will give the the length on 1 side of the CRYSTAL so we divide by 2
- Messages
- 639
- Reaction score
- 3,684
- Points
- 253
but its not tomorrow. o_o
Ohh, i meant for chem studentsYo, it ain't tomorrow.
- Messages
- 473
- Reaction score
- 1,511
- Points
- 153
My mistake... Answer is B... It's the cell with which the voltmeter is connected not the resistor... So Emf coming out of the cell and across the 15 ohm resistor is 7.5V... Then by using the formula I=V/R =7.5/15 , we will get .5 A current...Answer is B but I don't know how
- Messages
- 639
- Reaction score
- 3,684
- Points
- 253
q.9
Displacement is distance from starting point regardless of how much da body has travelled.
Distance with direction from 0 to 3 s is (1/2) * 3 * 30 = 45 m
Distance with direction from 3 to 5 is (1/2) * 2 * -20 = -20 m
So final distance from starting point = 45 - 20 = 25 m
Answer: B
Last edited:
- Messages
- 639
- Reaction score
- 3,684
- Points
- 253
q.9
Displacement is distance from starting point regardless of how much da body has travelled.
Distance from 0 to 3 s is (1/2) * 3 * 30 = 45 m
Distance from 3 to 5 is (1/2) * 2 * -20 = -20 m
So final distance from starting point = 45 - 20 = 25 m
Answer: B
Der is another way of solving dis too but its slightly more complicated
- Messages
- 90
- Reaction score
- 34
- Points
- 28
thanx alotbdensity=mass/volume
total mass will be 3.5*10^-25* 8 for 1 cube
and so Volume=9.2*10^-25 * 8/(9.2*10^3)
this will give the volume cube root the volume will give the the length on 1 side of the CRYSTAL so we divide by 2
- Messages
- 90
- Reaction score
- 34
- Points
- 28
- Messages
- 22
- Reaction score
- 20
- Points
- 13
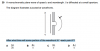
http://papers.xtremepapers.com/CIE/...nd AS Level/Physics (9702)/9702_s12_qp_12.pdf
QUESTION NUMBER 29
After what time will some portion of the wavefront XY reach point P?
ASAP!
QUESTION NUMBER 29
After what time will some portion of the wavefront XY reach point P?
ASAP!
- Messages
- 22
- Reaction score
- 20
- Points
- 13
- Messages
- 90
- Reaction score
- 34
- Points
- 28
- Messages
- 90
- Reaction score
- 34
- Points
- 28
T=wave length/velocityhttp://papers.xtremepapers.com/CIE/Cambridge International A and AS Level/Physics (9702)/9702_s12_qp_12.pdf
QUESTION NUMBER 29
After what time will some portion of the wavefront XY reach point P?
ASAP!
they are 3 waves so
T=3 wave length/C
THE ANSWER IS (C)