- Messages
- 704
- Reaction score
- 3,888
- Points
- 253
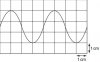
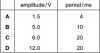
Thanks Thanks Thanksit's the diameter which has the largest effect. Look in the equation, d is a squared quantity. So the %age uncertainty in d would need to be doubled. So it will have the largest effect.